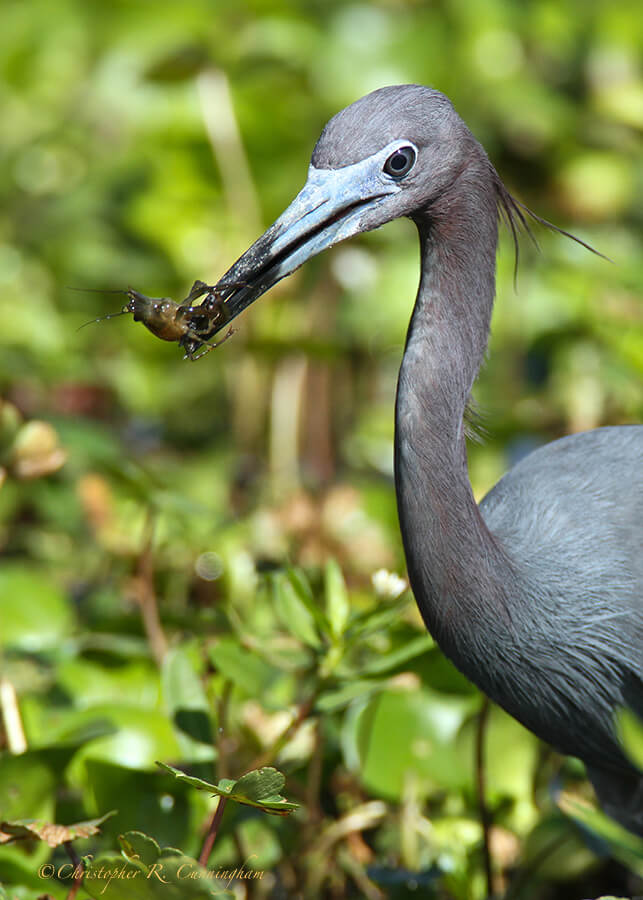
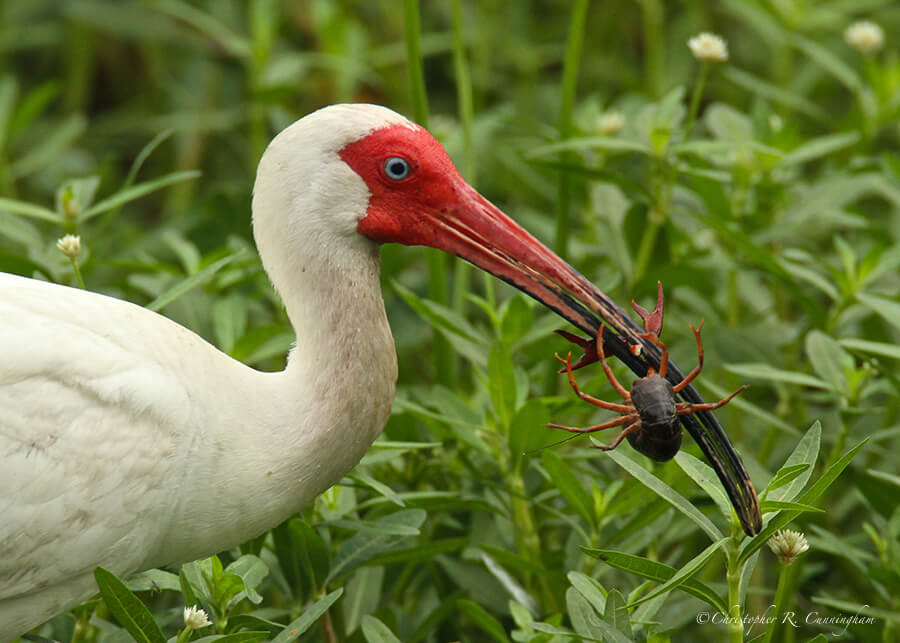
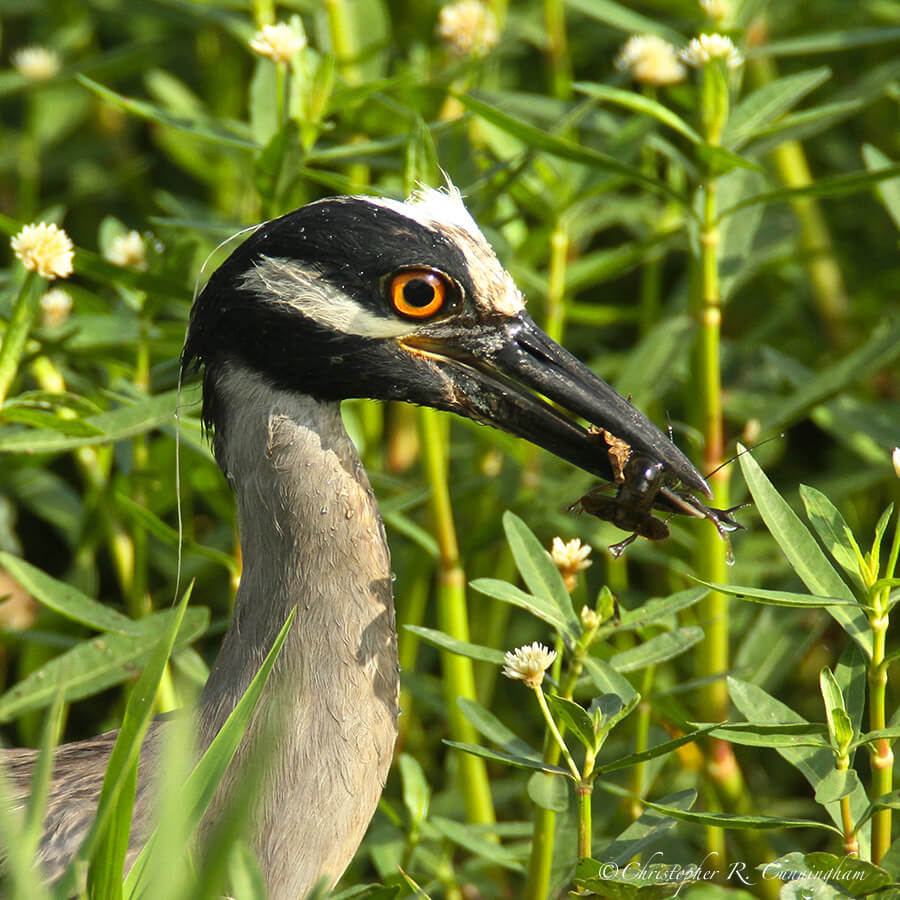
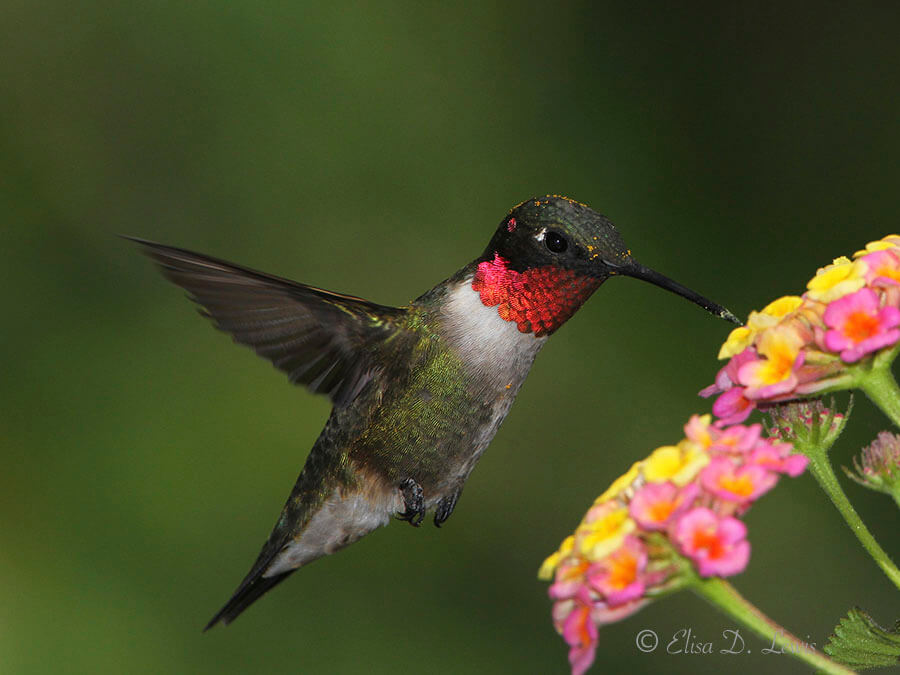
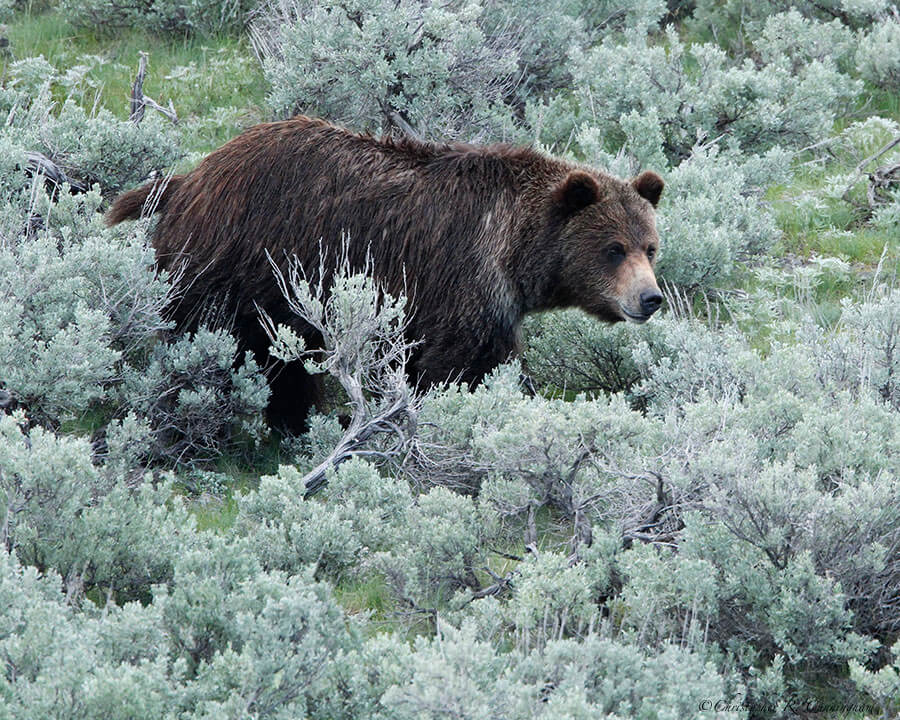
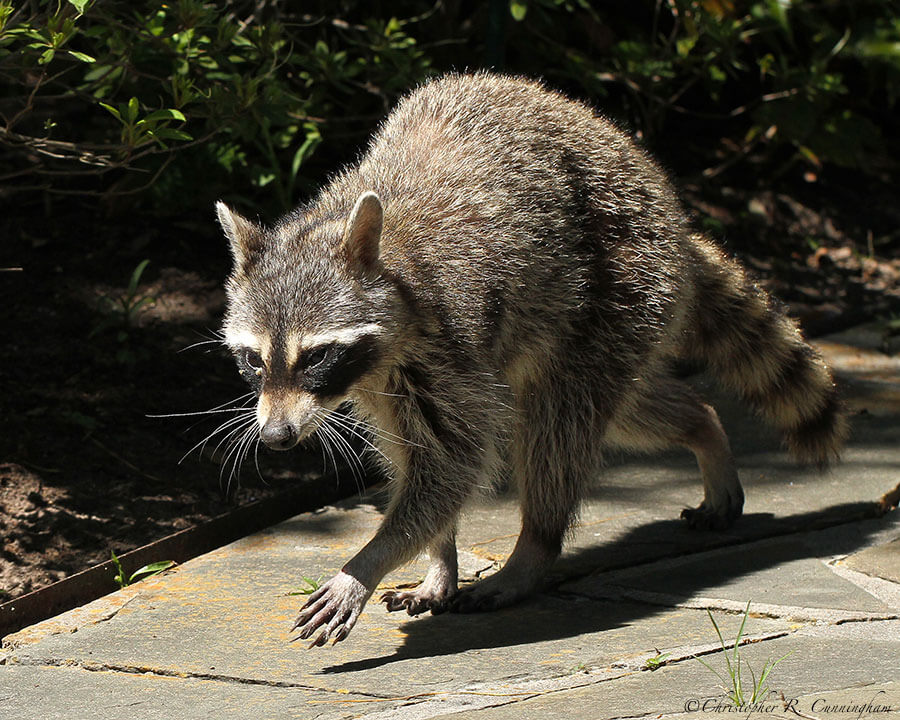
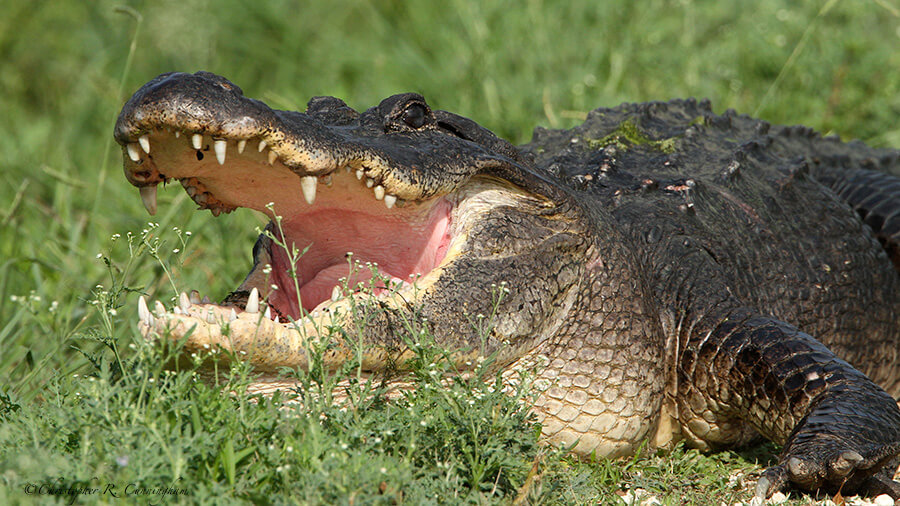
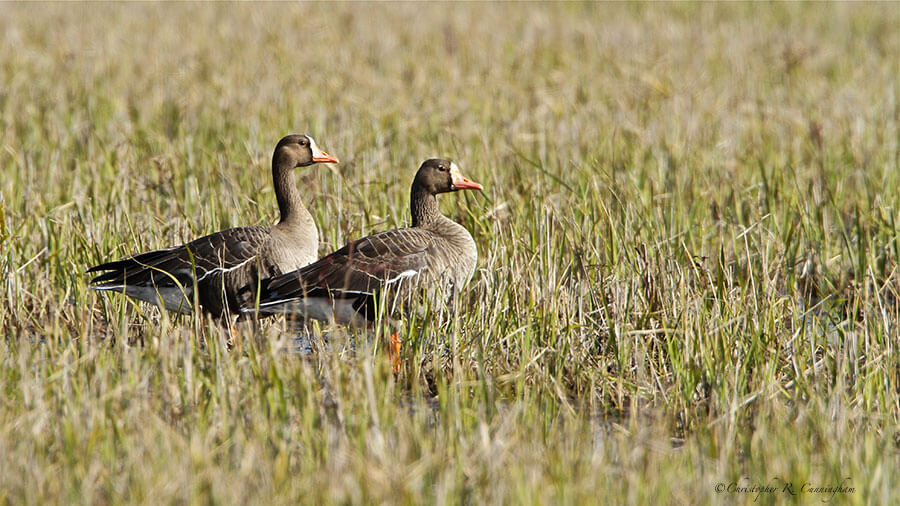
What we observe is not nature itself, but nature exposed to our method of questioning.—Werner Heisenberg
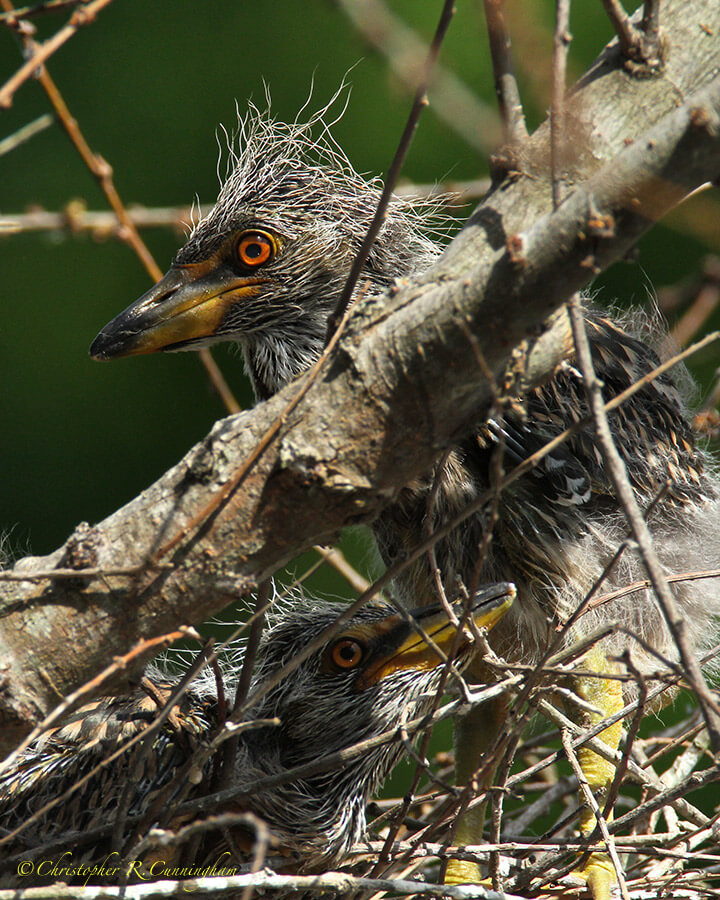

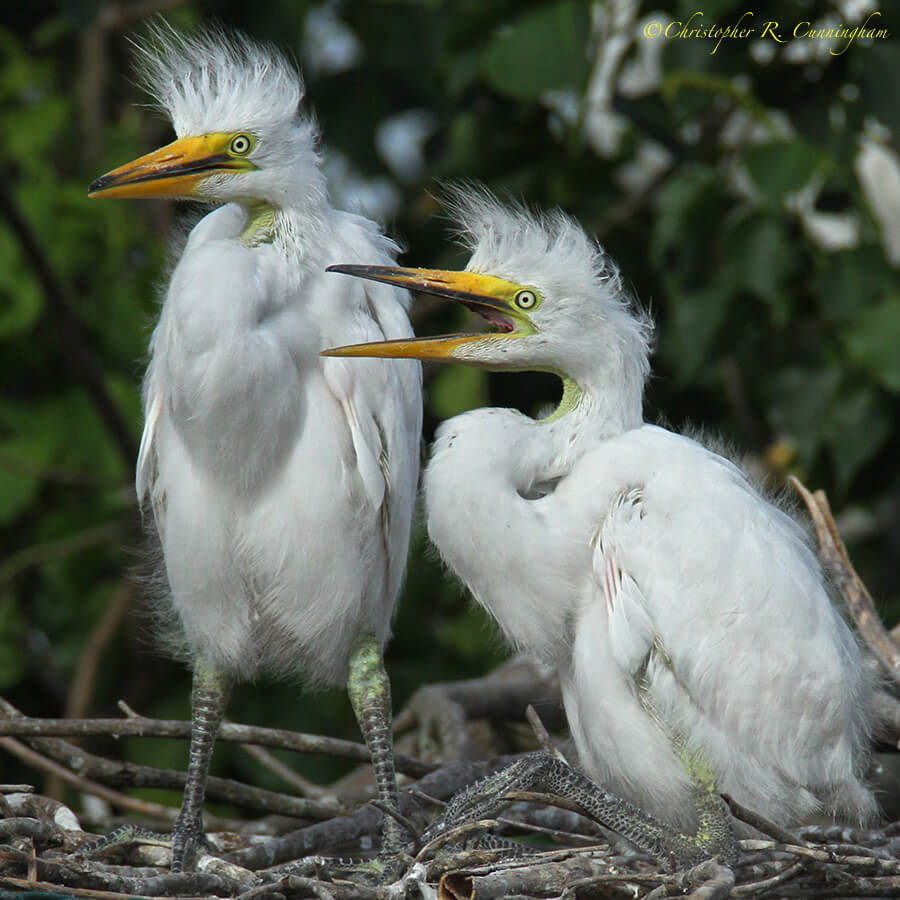
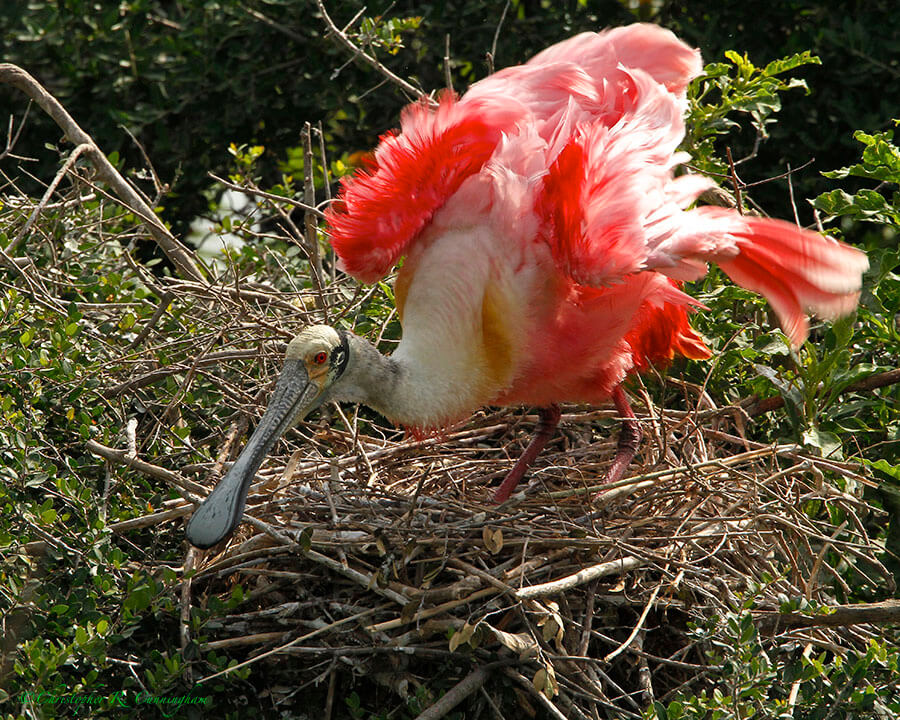
Photographing nesting birds has many of the challenges of other types of bird photography–and a few of it’s own. On the technical side, nests are typically made of sticks (although not always) so nest shots often have the “stick-in-face” problem–like the image shown above. Many bird species also nest well above eye-level in trees, so, short of going to extraordinary lengths, you’re not going to get any good nest shots of many species. More significant, though, are the ethical concerns that come up in the course of nest photography.
Once you’ve found a nest, you know where to look for the action. There’s no chasing birds around in the brush! At first, this seems like this will make for getting great photographic results easily. A little consideration, however, reveals that this is decidedly not the case.
Normally when photographing birds one tries to get as close as possible. If the bird becomes annoyed it will simply fly (or run) off. Obviously nestlings can not flee, so the photographer or observer must use personal discipline to keep an ethical distance. And the duration of the observation must also be taken into account. Unless I’m somewhere like Smith Oaks where the birds are used to being observed all day long by large numbers of observers, after a few minutes of shooting, I’m on my way. Furthermore, although there is no evidence that the use of flash injures wildlife, it is logical that it should not used on nesting birds lest parents and young birds be unduly stressed.
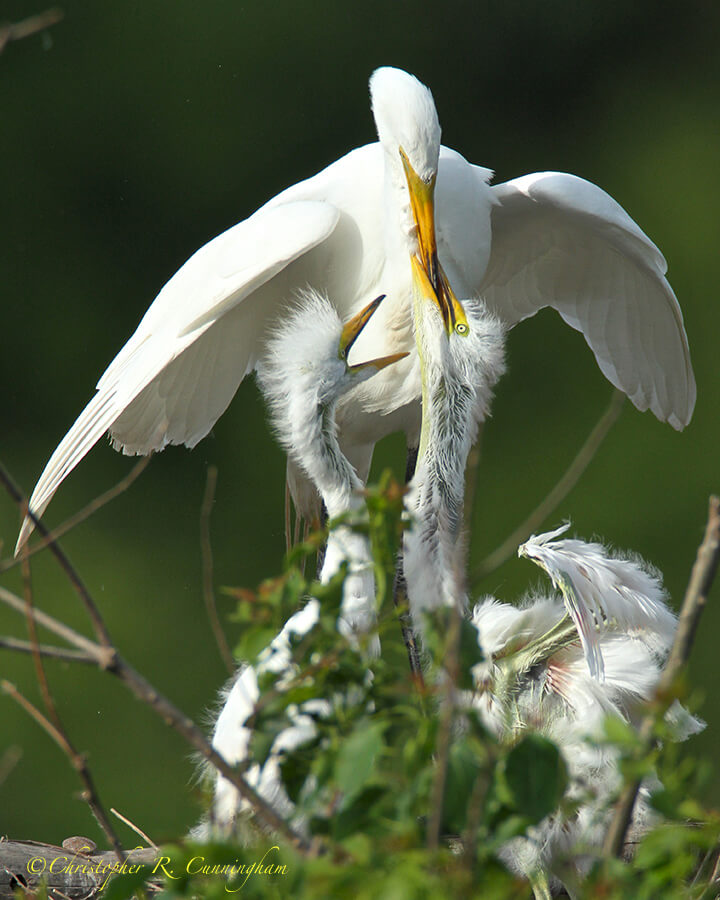

One last philosophical point: We must concede that most of the time we do not really know how birds behave in their natural state. If we are observing them (and their perceptions are much sharper than ours), then they know we are watching and are likely behaving accordingly. Ironically, then, it would seem that places like Smith Oaks where many thousands of birders visit during the nesting season may provide the most “natural” viewing experience as birds simply learn to tune out the human throng completely and go about their business.
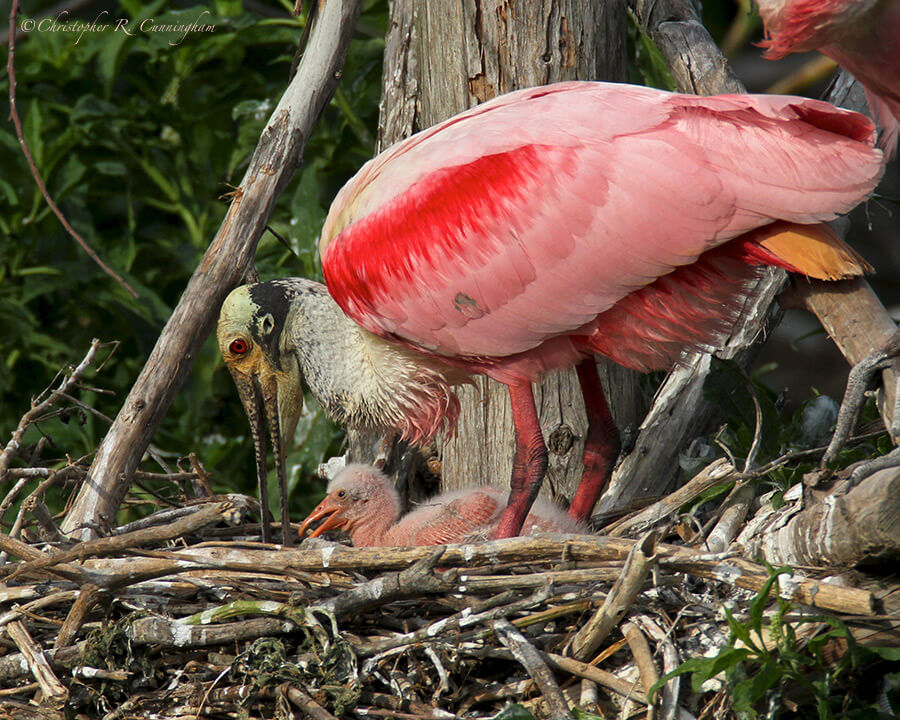

As far as I can judge, not much good can be done without disturbing something or somebody.—Edward Blake
©2014 Christopher R. Cunningham. All rights reserved. No text or images may be duplicated or distributed without permission.